Pharmacokinetics
 |
 |
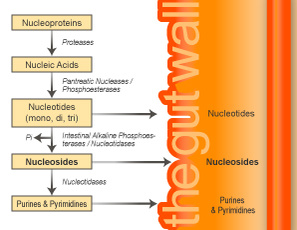
RNA is digested in the small intestine via the action of the pancreatic enzyme ribonuclease to the nucleotides adenosine-5'-monophosphate (AMP), guanosine-5'-monophosphate (GMP), cytidine-5'-monophosphate (CMP) and uridine-5'-monophosphate (UMP).
These nucleotides are then hydrolyzed to the nucleosides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine and uridine, respectively, via the action of the enzymes alkaline phosphatase and nucleotidase.
The nucleosides may be further hydrolyzed to the purine bases adenine and guanine and the pyrimidine bases cytosine and uracil.
The nucleosides are transported in the enterocytes by both facilitated diffusion and sodium-dependent carrier mediated processes.
Under normal conditions, that is, under conditions where the body is not under metabolic stress, the nucleosides undergo extensive catabolism in the enterocytes.
The end product of purine catabolism is uric acid.
An end product of pyrimidine metabolism is beta-alanine.
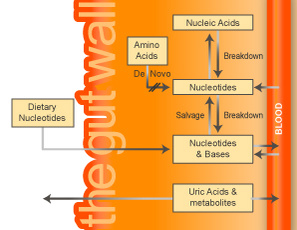
Nucleosides and bases that are not catabolized in the enterocytes are transported via the portal circulation to the liver, where they are also catabolized. A small percentage of ingested RNA and nucleotides reach the systemic circulation and is transported to various tissues of the body.
Even under normal conditions, a small percentage (from 2% to 5%) of dietary RNA and dietary nucleotides is incorporated into nucleic acids, especially in the small intestine, liver and skeletal muscle. This occurs via the salvage pathways of purine nucleotide and pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis.
During conditions of metabolic stress, including trauma, rapid growth and limited food supply, there is apparently greater conversion of dietary RNA and nucleotides into tissue nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA is digested in the small intestine via the action of the pancreatic enzyme deoxyribonuclease to deoxynucleotides; these, in turn, are hydrolyzed to deoxynucleosides and finally to the pyrimidine bases cytosine and thymine and the purine bases adenine and guanine.
The deoxynucleosides and bases are absorbed by the enterocytes and processed as described above for the nucleosides.
